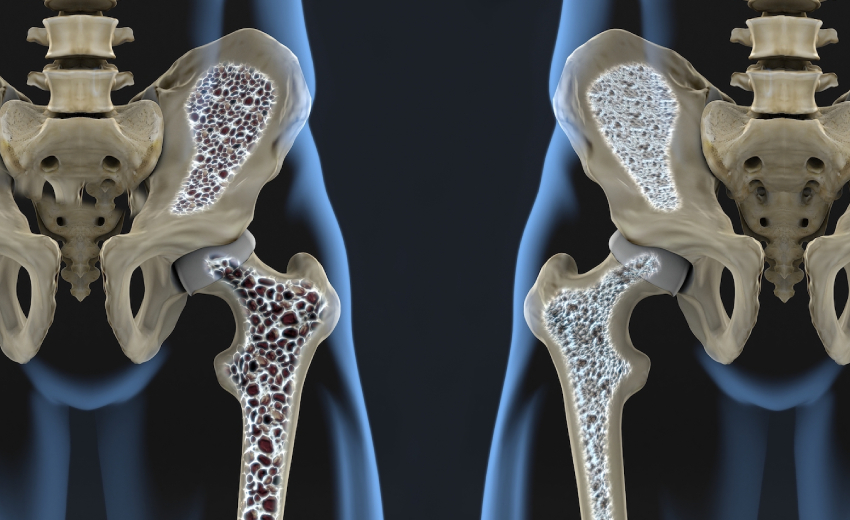
Osteoporosis or a “porous bone” as known in Latin is a condition that affects your bones. Osteoporosis commonly affects bones in the hips, ribs and the wrist and spine bones. Though it can occur in patients of all ages, it is more common among senior adults and those suffering from certain neurological disorders. Spinal cord injuries, Parkinson’s disease, multiple Sclerosis, and Strokes are the neurological conditions that can cause osteoporosis. These patients are more susceptible to falls and fractures due to osteoporosis. This article tours you through various neurological disorders and their impact on bone conditions. In case you come across any symptoms, it is advisable to consult Neuro doctors or a neurosurgeon with experience..
Neurological disorders and osteoporosis
A healthy bone typically has small spaces like a honeycomb. The osteoporosis increases the size of these spaces, causing the bones to lose their density and strength. Not only that, but the loss of minerals like Calcium can also result in weakening and thinning of the bones. In neurological disorders like Multiple Sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease, the loss of Calcium is prominent because of the increased inactivity. Then, the use of steroids in Multiple sclerosis adds further to the weakening of the bones.
The sudden neurological issues like spinal cord injuries and stroke can deteriorate the condition of the bones quickly after the injury. These patients lose considerable mineral density after the injury, and gradually, the loss increases over time. Paraplegia patients may lose essential minerals in the affected part of the body and thereby weaken that part.
Diagnosis
Though the significant factor that contributes to the variable bone density is genetic, exposure to corticosteroids and high rate of immobility are also considered as two other essential reasons in patients with neurological disorders. DXA scanning is the most widely available tool that is used to assess the fracture risk and osteoporosis in patients. The T Score or peak mass bone score is used by WHO to define osteoporosis based on DXA readings. T Score of -2.5 is considered as the Fracture threshold, below which there is a 90% chance of fractures. The patients are recommended to consult their neuro doctors with DXA readings to assess their conditions. Look out for the best neuro doctors or neurosurgeon in Chennai for a proper assessment. To know more about the impact of neurological conditions on bone health, continue reading the following section.
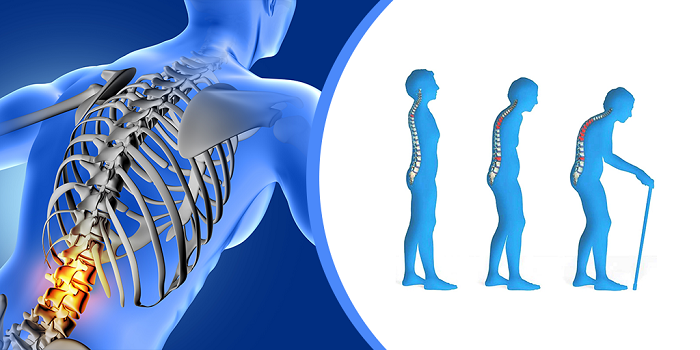
Impact of neurological conditions on bone health
Spinal cord injuries and effects
It is found that the spinal cord injuries that lead to paralysis can cause a rapid increase in bone resorption. Bone resorption is the process by which bones are absorbed and broken down by the body. During the breakdown, the minerals like Calcium and phosphorus are released into the blood, thereby weakening the bones. The patients are observed to show a lower hip bone density than the spine bones.
Epilepsy
An epileptic patient tends to show a higher risk of fracture. Studies show about 25% of fractures of epileptic patients were related to fits. The usage of phenobarbital and phenytoin is also another reason for the fracture risks in these patients. The case of Frank Osteomalacia is prominent among the patients who are administered the drugs mentioned above. The drugs have shown to increase metabolism and thereby result in the loss of Vitamin D.
Falls
According to the studies in neuro-rehabilitation units, falls are the common cause of fracture among the patients. The falls are attributed to the inability to rise from chairs, the prolonged use of benzodiazepines and poor depth perception. Those being administered the anticonvulsant drug is found to have double the risk of hip fractures.
Impact of steroids
The effects of steroids and functional disabilities are also prevalent in neurological conditions. Corticosteroid that is widely used for respiratory diseases is found to cause bone loss due to reduced calcium absorption and increased urinary calcium excretions. The use of steroids in multiple sclerosis to treat relapses has found to increase the risk of osteoporosis. A study among myasthenia patients who are steroid-treated has shown minor bone loss tendencies.
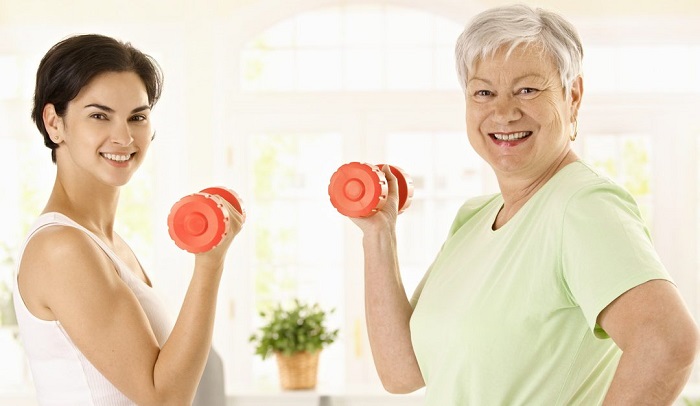

Treatment and prevention
Treatment
Alternate day steroid therapy has been widely used in the experiment, though there is no evidence of any significant benefits over equivalent daily doses. Non-steroid procedure identifies hormone replacement therapy and administering of bisphosphonates, calcitriol, Calcium and vitamin D, and calcitonin as treatment agents, as an effective treatment for osteoporosis in neurological conditions.
Non-pharmacological approaches like balance training and hip protectors have shown the prevention of falls and fractures to more significant effect. Weight-bearing exercises have also shown great benefits.
Check Out – About Treatments of osteoporosis increase bone material strength index in patients with low bone mass.
Prevention
Ensure that you eat a properly balanced diet and get enough sunlight to consume enough Vitamin D. It is also found that reduced mobility among neurological patients results in bone health deterioration. Exercises can immensely prevent the loss of bone minerals, and it is recommended to start after the injury. Request the help of an experienced physiotherapist for an effective exercise regime.


